Whole Body Lymphatic Drainage and Its Role in Holistic Body Care
Through the lens of wellness, body care is often reduced to skin-deep routines: exfoliating, cleansing, and cleansing and serums to polish the outer shell. True body care goes deeper. Holistic wellness involves turning the body’s internal systems and supporting them in ways that enhance long-term vitality. A historically overlooked but up-and-coming practice in systematic bodily support is whole body lymphatic drainage.
What Lymphatic Drainage?
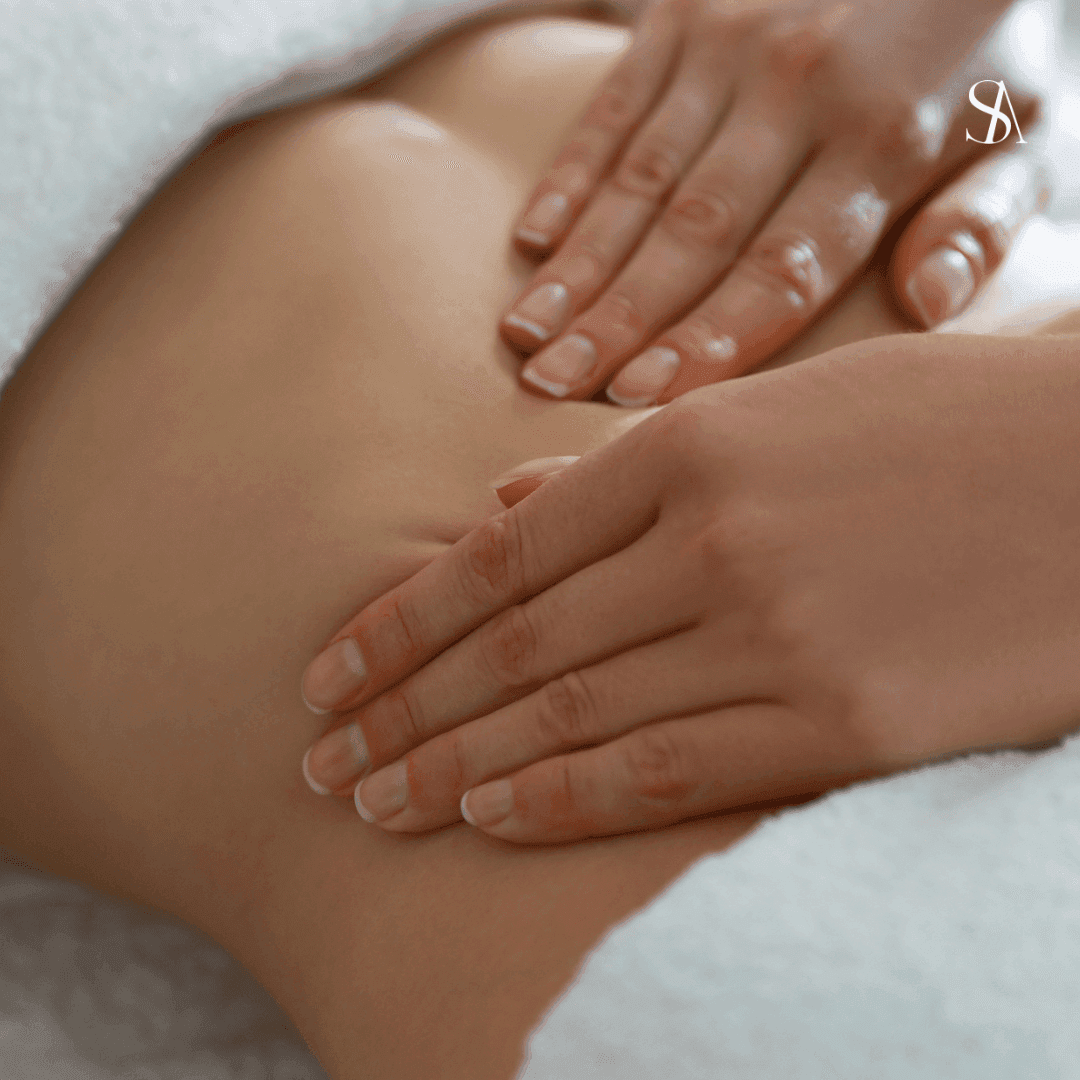
Lymphatic drainage is a technique that moves fluid and toxins from bodily tissue into the lymphatic system — a collection of nodes and vessels just below the skin. The lymphatic system then moves the fluid and toxins into the bloodstream, kidneys, and liver to be metabolized or excreted via saliva or urine.
Unlike blood, which is pumped by the heart, and food, which is moved by the intestines, lymph fluid requires manual stimulation to keep flowing. This can be achieved through compression garments, exercise like jumping or standing on a vibration plate, or, as mentioned — lymphatic drainage massage.
The Benefits of Lymphatic Drainage
Lymphatic drainage is often associated with reducing swelling in instances of post-surgery or pregnancy, but its benefits extend much further. When practiced regularly, whole body lymphatic drainage can:
- Detoxify the body to support immune function: reduces the risk of lymph node swelling so the lymphatic system can function more effectively
- Promote relaxation via soothing massage techniques
- Improve skin health from increased circulation: supply more oxygen to the skin, which promotes cell renewal and skin barrier healing
- Reduce of inflammation and edema (fluid retention) by promoting the flow of lymph fluid around and out of the body
Why This Matters for Body Care
Proactivity. Contemporary body care routines tend to be reactive: fix the breakout, smooth the bump, and cover the fatigue. Lymphatic drainage, however, reframes body care as proactive. It supports the body in doing what it was designed to do — cleansing, repairing, and renewing itself.
When integrated into a body care routine, whole-body lymphatic drainage creates a foundation for everything else: products absorb better, skin glows brighter, bloating reduces, and digestion speeds up. In this way, lymphatic health is a bridge between internal wellness and external beauty.
Lymphatic Drainage as Ritual
Incorporating whole body lymphatic drainage doesn’t have to be a chore — make it a ritual. Using chic tools, or just somebody oil and your own two hands, practice self-love and body care in the morning or before a shower. Whether you are dry-brushing, using gua sha, or incorporating mindful movement, these rituals are slow, mindful practices that encourage you to feel into your body, not just look at it.
Practical Ways to Support Lymphatic Health
If fancy tools aren’t accessible, or just not your style, here are a few virtually free ways to encourage lymphatic drainage for the whole body:
- Stay Hydrated: Lymph fluid needs water to move
- Get Moving: walking, stretching, and bouncing all stimulate lymph movement
- Breath Work: practice breathing techniques like the Breath of Fire; the diaphragm functions as a pump for the lymph system
- Dry Brush: literally. Use a dry body scrubber, clean hair brush (we won’t judge) or even a soft dish brush and gently circulate over the entire body moving towards the heart — bonus: dry brushing exfoliates!
- Massage Gently: look up videos on self-massage for lymphatic drainage
Rethinking Body Care
Whole body lymphatic drainage invites us to reimagine what body care really is. Instead of a surface-level act, it becomes a dialogue with the body that encourages overwell wellness. By supporting the lymphatic system, we are reminded that beauty and wellness are not skin deep. They are rooted in how well the body functions, and how deeply we listen to what it needs.